Total Cost Curve for a Typical Firm
Does a firm s price equal marginal cost in the short run in the long run or both. It has three main features.
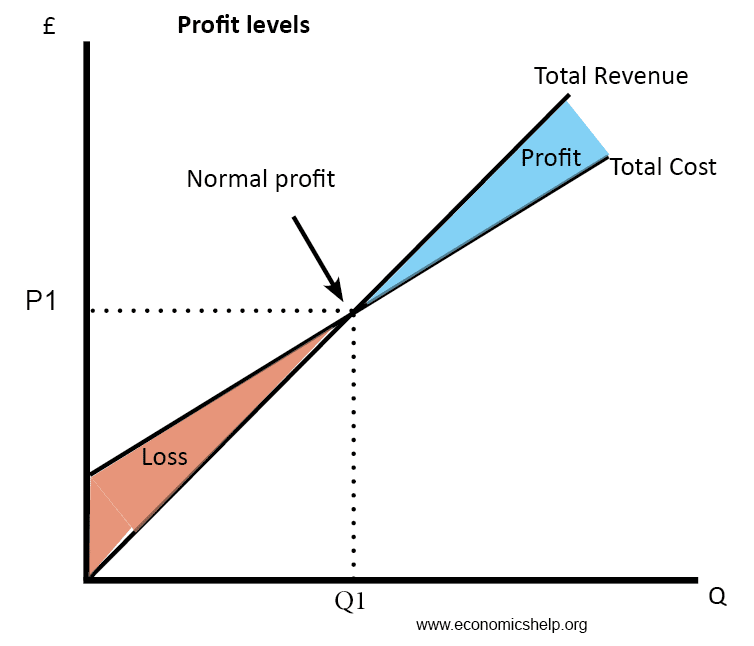
Diagrams Of Cost Curves Economics Help
Given the price is 20 what is the profit-maximizing output.
. Average fixed costs AFC decline continuously while average variable costs AVC decline reach a minimum and then increase resulting in a U-shaped average total cost ATC curve. Deriving the short-run supply curve Consider the competitive market for sports jackets. Average total cost curve above its marginal cost curve Ans.
This simply reflects the fact that it costs more in total to produce more output. Business Economics QA Library Draw the marginal cost and average total cost curves for a typical firm. At the output level of 5000 the average variable cost is 600 the average total cost.
A company in a competitive market has fixed costs of 200. The quantity of Stuffed Amigos production measured on the horizontal axis ranges from 0 to 10 and the average total cost incurred in the production of Stuffed Amigos measured on the vertical axis ranges from. Answer- Figure 6 shows the marginal-cost curve and the average-total-cost curve for a typical firm.
Explain why the curves have the shapes that they do and why they cross where they do. 10 20 30 40 50 60 Total Cost300 420 560 720 900 1100 a. The average cost of producing 5 cars Average total cost fracTotalspace costQuantity frac250000550000 Thus the value of average total cost is 50000.
A total cost curve is given in the table below. It has three main features. The marginal cost of the fifth car can be calculated as.
The total cost curve is upward sloping ie. For a perfectly competitive firm producing the profit-maximizing quantity the average total cost is 10 and the average variable cost is 8. The typical firms initial marginal-cost curve is MC1 and its average-total-cost curve is ATC1.
Average variable cost curve its marginal cost curve D. At the long-run equilibrium level of output this firms total cost A. Economies of scale because average total cost is falling as output rises.
Cannot be determined from the information provided. At what level of Q does the. Which of the figures represents the marginal cost curve for a typical firm.
Marginal cost curve above its average variable cost curve B. Draw the marginal cost and average total cost curves for a typical firm. The student earned 1 point in part biv for correctly drawing the firms average total cost ATC curve such that the MC curve passes through the minimum of the ATC curve and PATC when the firm is earning positive economic profit.
Does a competitive firms price equal its marinal marginal cost in the short run in the long run or both. In the long run Firm A incurs total costs of 1200 when output is 30 units and 1400 when output is 40 units. This isnt necessarily always the case- the total cost curve could be linear in quantity for example- but is fairly typical for a firm for reasons that will be explained.
Firms average revenue curve as a horizontal line at the price determined by the market. The law of diminishing returns depends on the assumption that A. In the initial equilibrium the industry supply curve S1 intersects the demand curve at price P1 which is equal to the minimum average total cost of the typical firm.
The long-run average cost curve is a type of lower boundary of the short-run cost curves. Which of the figures represents the total cost curve for a typical firm. Marginal cost fracTotal space cost_5space - Total space cost_45-4 frac250000-2250005-4.
Qmax profit maximizing output. In the short run a firms supply curve is equal to the A. Typical Short-Run Average Cost Curve.
The firms marginal cost is MC Q 2 2. Which of the figures represents the marginal cost curve for a typical firm. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market.
Whenever marginal cost is greater than average total cost average total cost is rising. Refer to Figure 1. 2 average total cost is U-shaped.
The graph to the right is the average total cost curve for the short-run production of Wacky Willy Stuffed Amigos those cute and cuddly armadillos and tarantulas. 1 marginal cost is rising. Are market supply curves typically more elastic in the short run or in the long run.
At the point of intersection of MR and MC when we extend the line on to the x-axis we can plot the profit maximizing output Qmax. A firm in the soccer ball market has an output of 5000 balls which it sells for 10 each. The average total cost curve is constructed to capture the relation between cost per unit of output and the level of output ceteris paribus.
ATC average total cost. Average variable cost B. As industry output contracts each firms long-run average total cost curve shifts upward.
Marginal and average total cost curves. Does a firm s price equal the minimum of average total cost in the short run in the long run or both. The marginal cost MC curve intersects the ATC curve at the minimum ATC.
And 3 whenever marginal cost is less than average total cost average total cost is declining. Marginal cost above its average total cost curve C. Which of the figures represents the production.
Figure 6 shows the marginal-cost curve and the average-total-cost curve for a typical firm. This can be understood most easily by thinking of a series of short-run average total cost curves each one for a different level of the fixed input capital as shown in Figure 831. Refer to Figure 1.
The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. Long-run average total costs rise as output increases. 1 marginal cost is rising.
What is the profit. Suppose a firms total cost curve is given by the equation 2 TC Q Q 2 100. A perfectly competitive and productively efficient firm organizes its factors of production in such a way that the average cost of production is at the lowest point.
Figure 1 If Francos Pizza Parlor knows that the marginal cost of the 500th pizza is 350 and that the average total cost of making 499 pizzas is 330 then. The slope of the total variable cost curve equals a. Given the data answer the questions below.
The total cost curve is generally bowed upwards. The slope of the total variable cost curve equals A. A firm will produce output until its marginal revenue equals its marginal cost.
And 3 whenever marginal cost is less than average total cost average total cost is declining. Thus the typical firm earns no economic profit. Explain why the curves have the shapes that they do and why they cross where they do.
Firms in the market for soccer balls are selling in a purely competitive market. Draw the marginal cost and average total cost curves for a typical firm. Marginal physical product Ans.
Under what conditions will a firm exit a market. Whenever marginal cost is greater than average total cost average total cost is rising. The following graph shows the marginal cost MC average total cost ATC and average variable cost AVC curves for a typical firm in the industry.
2 average total cost is U-shaped.

0 Response to "Total Cost Curve for a Typical Firm"
Post a Comment